Diabetes and The Importance of Regular Blood Sugar Monitoring
Written by Anshul Rathore
Regular blood sugar checks are crucial for managing diabetes. It allows diabetics to monitor levels and adjust treatment plans to prevent complications. Talk to your healthcare provider about the frequency of monitoring.
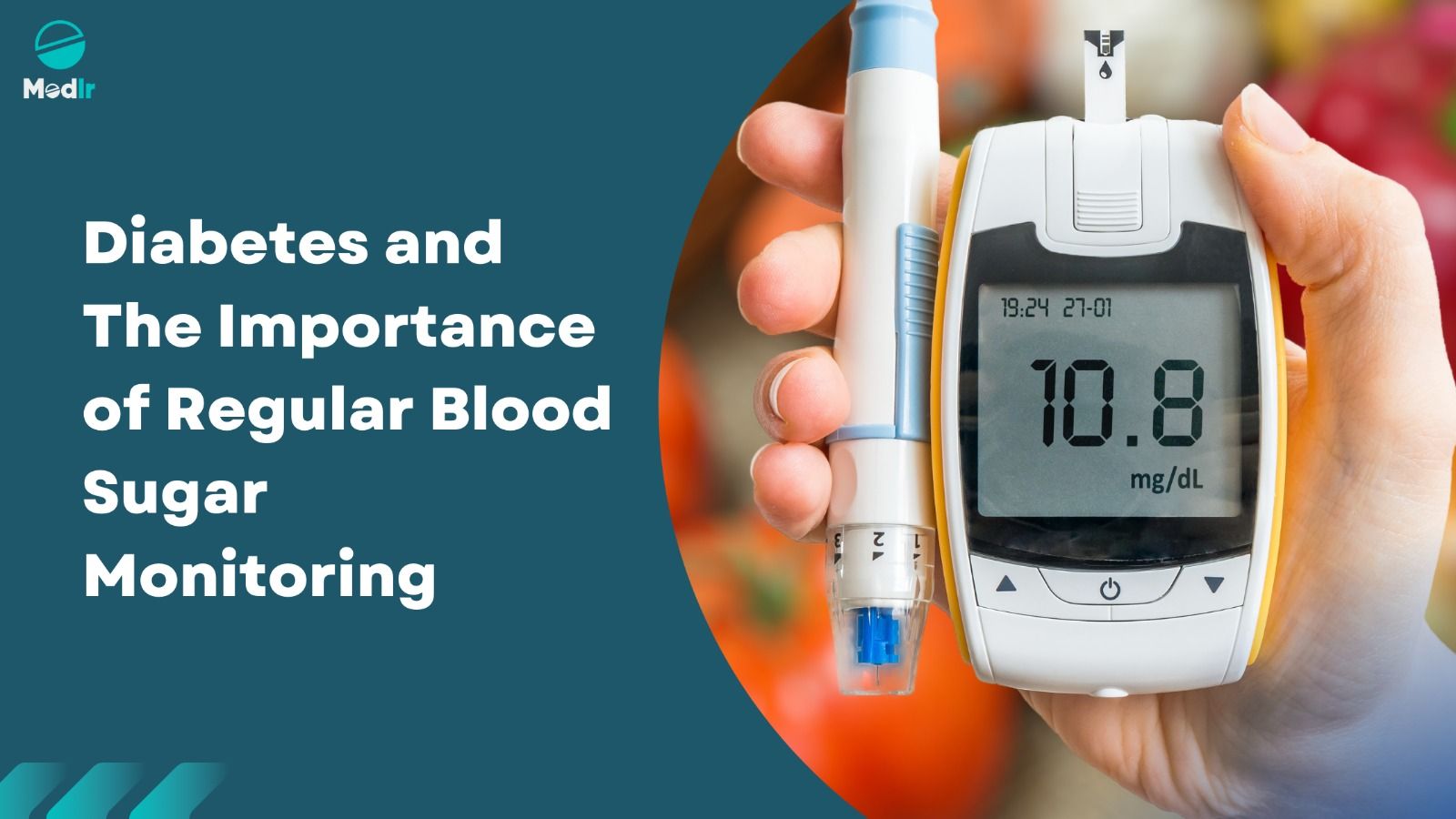
Millions of people around the world suffer from the chronic disease of diabetes. It occurs when the body is unable to produce or properly use insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. When left untreated, uncontrolled blood sugar levels can result in serious health problems like damage to the kidneys, heart, and nerves. The regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is one of the most crucial tools for managing diabetes.

What is blood sugar monitoring?
The process of monitoring blood sugar involves determining the amount of glucose (sugar) in the blood. Glucose is the body's primary energy source, but having too much or not enough can cause problems. In order to ensure that their blood sugar levels are within the desired range, diabetics must routinely check them.
Why is blood sugar monitoring important for people with diabetes?
Several factors necessitate that diabetics continuously monitor their blood sugar levels:
1. Insulin Dosage Adjustment: The hormone insulin controls blood sugar levels. Diabetes patients who use insulin injections must regularly check their blood sugar levels and adjust their insulin dosage as necessary. It can be dangerous to have hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) brought on by too much insulin. Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) brought on by insufficient insulin can result in complications.
2. To Identify Patterns: Monitoring blood sugar levels over time can help identify patterns in blood sugar fluctuations. For example, if blood sugar levels are consistently high after meals, changes to diet or medication may be necessary.
3. In Order to Prevent Complications: Long-term effects of high blood sugar levels can include kidney damage, heart disease, and nerve damage. Regular blood sugar monitoring can aid in preventing these complications by keeping blood sugar levels within the target range.
4. To Improve Quality of Life: When their blood sugar levels are within the target range, diabetics feel better and have more energy. People with diabetes who achieve and maintain good blood sugar control can improve their quality of life with the help of routine blood sugar monitoring.
How often should blood sugar be monitored?
Several variables, including the type of diabetes, the treatment strategy, and the patient's lifestyle, can affect how frequently blood sugar levels are monitored. While type 2 diabetics only need to check their blood sugar levels once or twice daily, type 1 diabetics frequently need to check it throughout the day.
Some factors that may affect blood sugar levels and require more frequent monitoring include:
- Illness or infection
- Changes in diet or activity level
- Stress
- Changes in medication or insulin dosage
The importance of routine monitoring is especially crucial for people with type 1 diabetes. Depending on their insulin regimen, diet, and level of physical activity, they should check their blood sugar levels at least four times per day and possibly more.
Even though type 2 diabetics may not require as much monitoring, it is still crucial to regularly check their blood sugar levels. They need to check their blood sugar levels before meals, after meals, or at particular times of the day depending on their treatment plan.
Together with your healthcare provider, you must decide how frequently to check your blood sugar. They'll consider your individual requirements and, if necessary, alter the frequency of your monitoring.
Tracking other diabetes-related metrics, such as blood pressure and cholesterol levels, is equally important to tracking blood sugar levels. You must visit your doctor frequently to make sure your diabetes management plan is working properly and to make any necessary adjustments.
Conclusion
Regular blood sugar checks are crucial for managing diabetes. It makes it possible for diabetics to keep an eye on their blood sugar levels and adjust their treatment plan as needed to prevent complications. If you have diabetes, be sure to talk to your healthcare provider about how frequently you should check your blood sugar levels and other pertinent measurements. When diabetes is properly managed and cared for, people with the condition can lead happy, healthy lives.
FAQs
What is the relationship between obesity and type 2 diabetes?
The connection between obesity and type 2 diabetes is strong. Obesity significantly increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. In fact, obesity is considered one of the most significant risk factors for this condition.
How does obesity contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes?
Obesity leads to an increase in insulin resistance, which means the body's cells become less responsive to insulin. This resistance results in higher levels of glucose in the blood, leading to the development of type 2 diabetes.
Does every obese person develop type 2 diabetes?
Not every obese person will develop type 2 diabetes, but the risk is significantly higher compared to individuals with a healthy weight. Other factors, such as genetics and lifestyle choices, also play a role in determining an individual's risk of developing the disease.
Can losing weight reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes?
Yes, losing weight can greatly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, especially for individuals who are overweight or obese. Even a modest weight loss of 5-10% can have a significant impact on reducing the risk.
Does obesity affect insulin production in the body?
Obesity can affect insulin production in the body. Over time, excess fat cells release certain chemicals that can disrupt the normal functioning of insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This can lead to decreased insulin production, further contributing to the development of type 2 diabetes.
Are there specific areas of the body where excess fat increases the risk of type 2 diabetes?
Yes, excess fat around the abdomen and waist, known as visceral fat, is particularly associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. This type of fat is metabolically active and releases substances that interfere with insulin action and glucose regulation.
Can obesity-related type 2 diabetes be reversed?
In some cases, obesity-related type 2 diabetes can be reversed or managed effectively through lifestyle changes. By adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight, individuals can improve their insulin sensitivity and blood glucose control.
Can medications help manage type 2 diabetes in obese individuals?
Yes, medications can play a crucial role in managing type 2 diabetes in obese individuals. Along with lifestyle modifications, doctors may prescribe oral medications or insulin to help regulate blood glucose levels and improve insulin sensitivity.